A simple REST API server
To view this content, buy the book! 😃🙏
Or if you’ve already purchased.
A simple REST API server
Background: Node, HTTP, JSON, MongoDB
We’ll start our process of understanding GraphQL by building a simple REST API using Node.js and the popular Express web framework. We’ll be retrieving data from a MongoDB database and using Mongoose as our object-document mapper to simplify querying the data we have stored (an ODM is the ORM equivalent for document databases).
Learn about MongoDB, the Node driver, and Mongoose in Background > MongoDB.
In this application, our server will listen for requests to the /users/:id URL. We use the ID passed as a parameter in the URL (as specified by the :id) to query a user record from the database and return it as a JSON string. If we encounter any errors, we return a 500 error, and if we can’t find the user, we return a 404—all standard REST practices.
const express = require('express')
const server = express()
// Get the Mongoose models used for querying the database
const { User } = require('./models.js')
// Listen for all GET requests to /users/:id URL (where the
// ID is the ID of the user account)
server.get('/users/:id', (req, res) => {
// Try to find the user by their id (_id field), using the ID
// parameter from the URL.
User.findById(req.params.id, (err, user) => {
if (err) {
// The DB returned an error so we return a 500 error
return res.status(500).end()
}
if (!user) {
// No user was found so we return a 404 error
return res.status(404).end()
}
// Return the user to the client (automatically serialized
// as a JSON string)
res.send(user)
})
})
// Start the application, listening on port 3000
server.listen(3000)The Mongoose data models are stored in a separate file:
const mongoose = require('mongoose')
// Connect to the local MongoDB database named "testdb"
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/testdb')
// Create a User schema to be stored in the MongoDB database
const UserSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
_id: String,
username: String
})
// Turn that schema into a model that we can query
const User = mongoose.model('User', UserSchema)
module.exports = { User }We connect to the database and implement a schema for the User that has two fields, _id (the default ID field for MongoDB) and username, and we turn that schema into a model that lets Mongoose know that users should be stored in the users collection (it takes the given model name 'User' and lowercases and pluralizes).
We’ll need to have some data in our database to start, so we’ll insert a couple of simple documents with string _id and username fields, looking something like this (in MongoDB Compass, a desktop graphical interface for running MongoDB queries against a database):
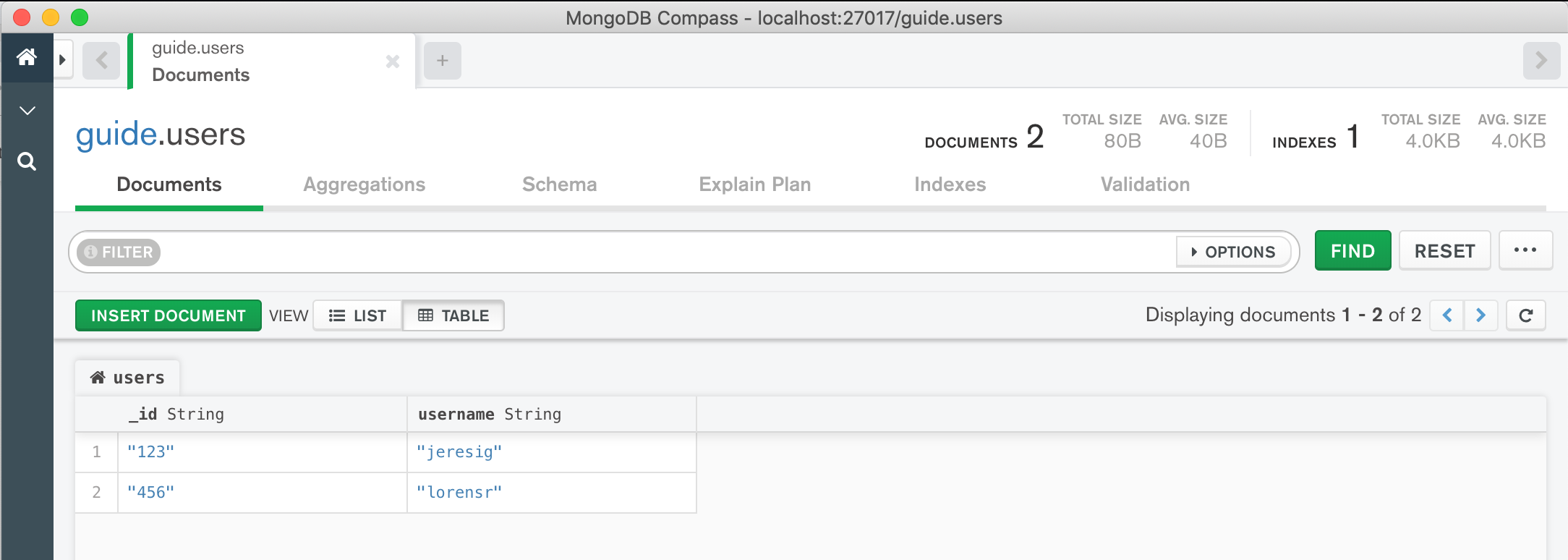 The two records stored in the “users” collection of the MongoDB database.
The two records stored in the “users” collection of the MongoDB database.
To query this endpoint would be quite simple—we can run curl from the command line to verify that the endpoint’s response matches our expectations:
$ curl http://localhost:3000/users/123
{"_id":"123","username":"jeresig"}
$ curl -I http://localhost:3000/users/abc
HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found
X-Powered-By: Express
Date: Sat, 02 Dec 2017 19:11:52 GMT
Connection: keep-aliveQuerying for a user by their ID returns the expected JSON object, and if we try to find a user that’s not in the database, we get the expected 404 error. Perfect!