Querying in production
Going through the different ways we can query our deployed GraphQL API
To view this content, buy the book! 😃🙏
Or if you’ve already purchased.
Querying in production
If you’re jumping in here,
git checkout 28_0.2.0(tag 28_0.2.0).
Now when we visit our app-name.herokuapp.com, instead of “Application error” we see:
GET query missing.Usually GraphQL requests are sent by POST, but Apollo Server also supports receiving GET requests. The browser is making a GET / request when we load the page, but the format that Apollo supports is GET /?query=X. Let’s test it with the { hello } query:
app-name.herokuapp.com/?query={hello}

This method of querying our production server works, but it becomes inconvenient if queries are large or use variables, and we can’t add an authorization header. The method we were using before, GraphQL Playground, is disabled by default in production. However, we can use the Playground app (download the latest .dmg or .exe file) to query any GraphQL API. First, we select “URL ENDPOINT” and enter our production URL:
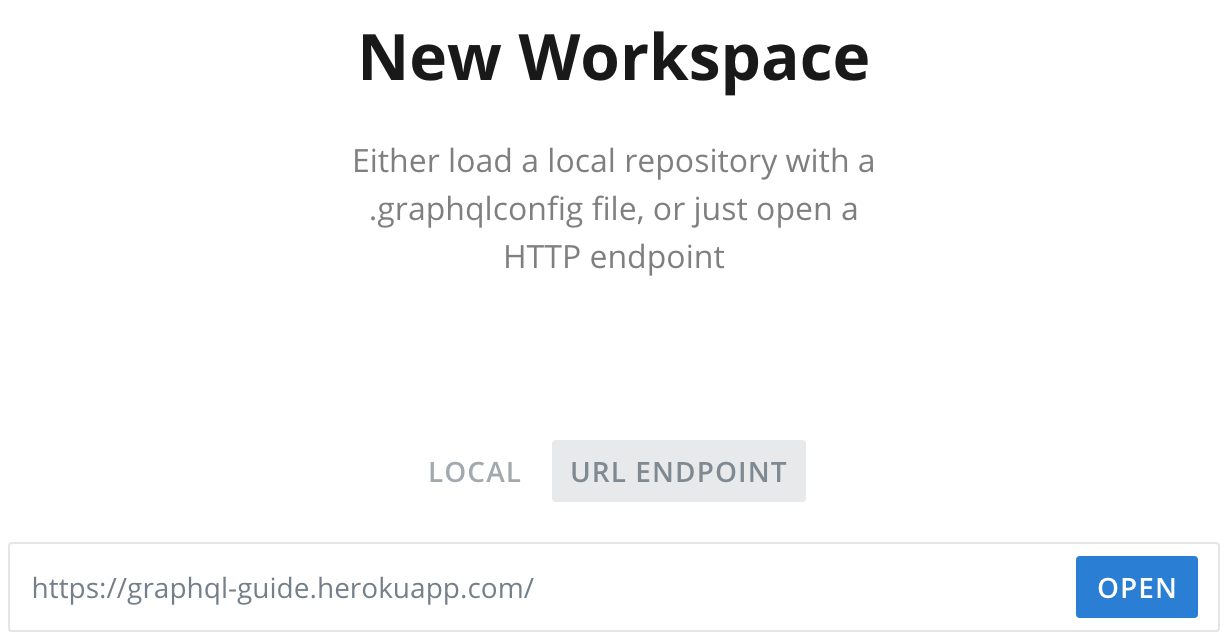
And then we query:
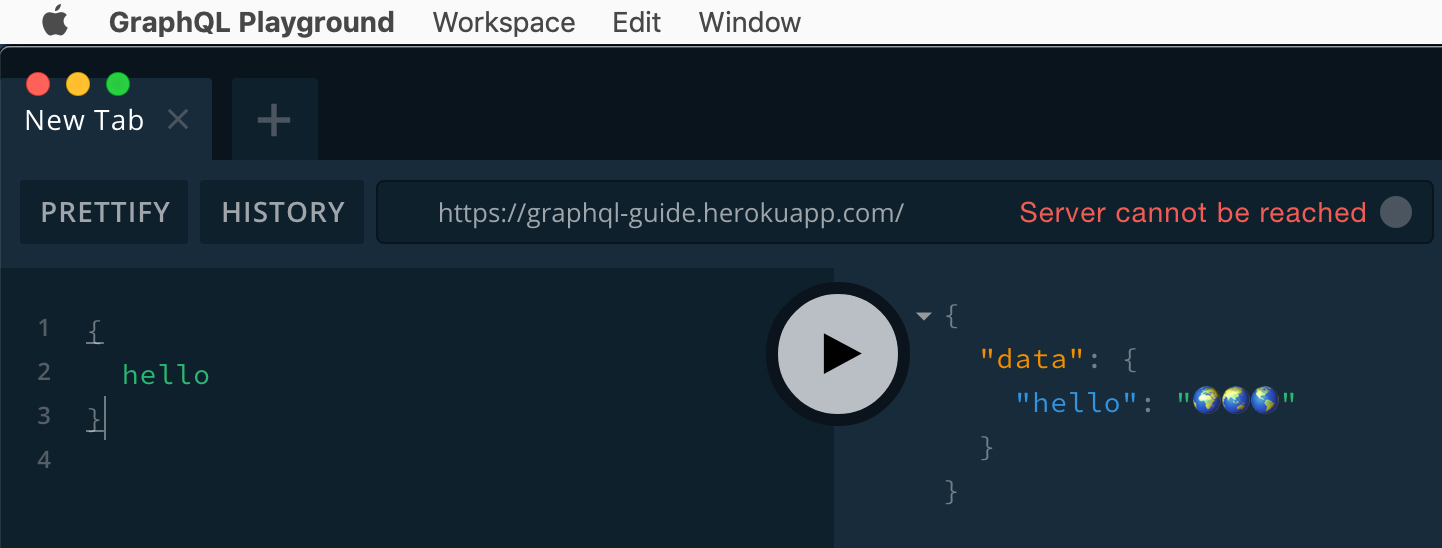
While the query returns a response, we see the “Server cannot be reached” error. Query autocompletion doesn’t work, and the schema tab doesn’t load. These issues occur because introspection—the queries that return the schema—is disabled by default in production in order to obscure private APIs.
Private APIs are meant to be used only by the company’s own applications, versus public APIs like the GitHub API that are meant to be used by third parties.
If we were publishing a public API that we wanted third-party apps to query, we would want to enable at least introspection (and probably Playground as well) to make it easier for the third-party developers to query our API.
We can enable both introspection and Playground in production by adding the last two options below:
src/index.js
const server = new ApolloServer({
typeDefs,
resolvers,
dataSources,
context,
formatError,
introspection: true,
playground: true
})$ git add src/index.js
$ git commit -m 'Enable introspection and Playground'
$ git push heroku 26:masterNow we can view the schema in the Playground app, and if we visit our index URL, the Playground website will load:
If we want to undo the change, we can do:
$ git reset HEAD^
$ git checkout -- src/index.js
$ git push heroku 26:master -fWe need the -f (force push). A normal push will fail because the heroku remote’s master branch is in a different state from our branch 26 (heroku still has the “Enable introspection and Playground” commit as the branch tip).
In summary, the ways we can interactively query our production GraphQL server are:
GET /?query=X- Playground app without introspection
- Playground app with introspection (the server must have introspection enabled)
- Playground website, if the server has it enabled
And we can, of course, continue to query it with POST requests on the command line or in code.